Swimmer's ear
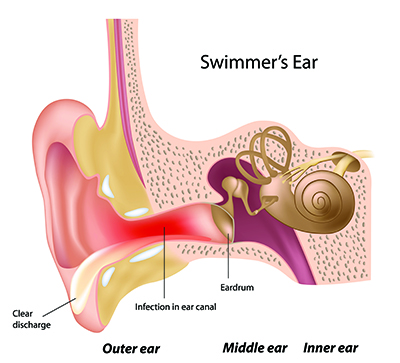
What is Swimmer's Ear?
Swimmer's ear, also known as otitis externa, is a painful condition that affects the outer ear and ear canal. It occurs when water remains trapped in the ear canal after swimming or bathing, creating a moist environment ideal for bacterial or fungal growth. This can cause inflammation, infection, and irritation, resulting in discomfort and pain.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Swimmer's ear occurs when bacteria or fungi multiply in the ear canal due to trapped water. Some factors that can increase the risk of developing swimmer's ear include:
1. Water exposure: Prolonged exposure to water, such as swimming or frequent bathing, increases the risk of trapped water in the ear canal.
2. Damaged skin: Any damage to the skin lining the ear canal, such as from scratching or using cotton swabs, can create an entry point for bacteria or fungi.
3. Humid climate: Living in a humid climate can increase the likelihood of developing swimmer's ear.
4. Allergic reactions: Some individuals may have an allergic reaction to certain substances in the water, such as chlorine or other chemical additives.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of swimmer's ear can vary in severity and may include:
1. Ear pain: Swimmer's ear is often accompanied by severe ear pain, which may worsen when pulling on the earlobe or moving the jaw.
2. Itching: Persistent itching in the ear canal is a common symptom of swimmer's ear.
3. Redness and swelling: The affected ear may appear red, swollen, and inflamed.
4. Discharge: In some cases, there may be yellowish or greenish discharge from the ear canal.
5. Decreased hearing: Due to the swelling and inflammation, temporary hearing loss or muffled hearing can occur.
Treatment Options:
If you suspect you have swimmer's ear or experience any of the above symptoms, seeking professional evaluation from an experienced Otolaryngologist like Dr. Seejo George is crucial. Treatment options for swimmer's ear may include:
1. Ear cleaning: Dr. George may gently clean the ear canal to remove any trapped water or debris, facilitating healing and reducing symptoms.
2. Ear drops: Antibiotic or antifungal ear drops may be prescribed to help clear the infection and reduce inflammation.
3. Pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help manage the pain associated with swimmer's ear.
4. Avoidance of water exposure: During the healing process, it is important to keep the affected ear dry and avoid water exposure, which can exacerbate symptoms.
Prevention:
To prevent swimmer's ear in the future, consider the following preventive measures:
1. Keep the ears dry: After swimming or bathing, gently dry your ears with a towel or use a hairdryer on a low setting to remove any moisture from the ear canals.
2. Use earplugs: If you frequently swim or engage in water activities, consider using waterproof earplugs to prevent water from entering the ear canals.
3. Avoid inserting objects into the ears: Refrain from using cotton swabs or any other objects to clean the ears, as they can damage the ear canal, increasing the risk of infection.
4. Use ear drops: After water exposure, instill a few drops of alcohol-based ear drops to help evaporate any trapped water and inhibit bacterial or fungal growth.
5. Maintain good ear hygiene: Keep your ears clean and dry, but avoid excessive cleaning that may remove the natural protective layer of the ear.
Conclusion:
If you suspect you have swimmer's ear or are experiencing symptoms such as ear pain, itching, or redness, seeking professional help from a skilled Otolaryngologist like Dr. Seejo George is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. With Dr. George's expertise and compassionate care, you can receive the best treatment options for swimmer's ear, relieving your symptoms and preventing future occurrences. Contact us to schedule an appointment or to learn more about swimmer's ear and its management.